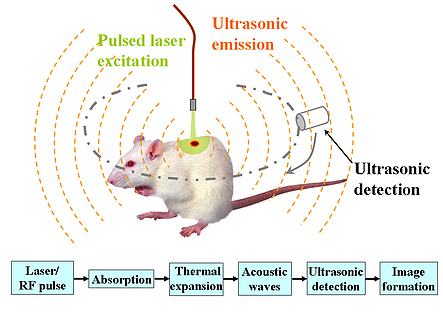
Photoacoustic imaging (also called optoacoustic or thermoacoustic imaging) is a powerful noninvasive imaging modality and has the potential to image animal or human organs, such as the blood structure of breast and the brain, with simultaneous high contrast and high spatial resolution. it also allows a depth imaging up to several centimeters in biological tissue.
The photoacoustic (PA) effet is the physical basis for PA imaging; it refers to the generation of acoustic waves by the absorption of electromagnetic (EM) energy, such as optial or radio-frequecy(RF) waves.Alexander Graham Bell first reported the observation of sound generated by light in 1880.
 by WIKIPEDIA
by WIKIPEDIA
 (a)
(a)
 (b)
(b)
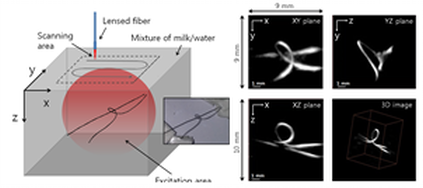
(a) Schematic of the PET fibers phantom (inset: photograph of the PET fibers phantom before adding of mixture of milk/water). (b) 3D Photoacoustic images of the PET fibers phantom. Top left: XY plane maximum intensity projection image (MIP) of 3D photoacoustic image. Top right: YZ plane MIP image. Lower left: XZ plane MIP image. Lower right: 3D image (Video 1) of reconstructed PET fibers phantom.
 (a)
(a)
 (b)
(b)
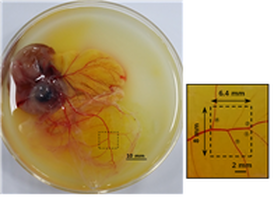
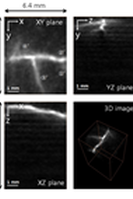
(a) Photograph of blood vessels on chicken chorioallantoic membrane (CAM). Dotted box is Scanning area of 6.4 mm x 8 mm. (b) 3D Photoacoustic images of the blood vessels on chicken CAM. Top left: XY plane maximum intensity projection image (MIP) of 3D photoacoustic image. Top right: YZ plane MIP image. Lower left: XZ plane MIP image. Lower right: 3D image (Video 1) of the reconstructed blood vessels on chicken CAM (Video 2, MPEG, 16 MB).